go基础数据结构 hashmap数据结构与实现原理
原文地址:https://www.douyacun.com/article/0e0f6fd564d44073a6ef757089f9d14d
通过数据结构、实现原理、读写操作来了解go hashmap
数据结构
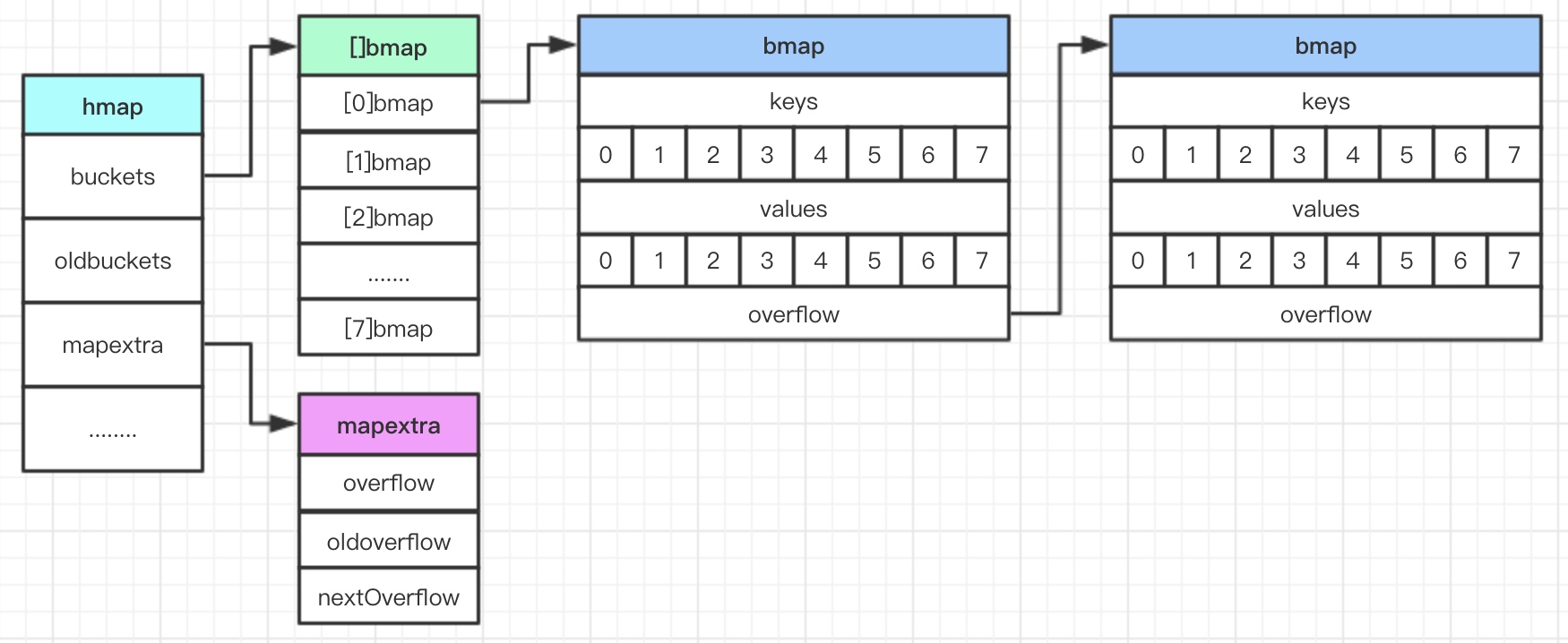
hash有2个关键数据结构: hmap bmap
hmap: runtime/map.go
type hmap struct {
count int
flags uint8
B uint8
noverflow uint16
hash0 uint32
buckets unsafe.Pointer
oldbuckets unsafe.Pointer
nevacuate uintptr
extra *mapextra
}
count元素数量B2^B个buckets桶noverflowbuckets溢出桶的数量,近似值buckets桶oldbuckets扩容时指向原buckets桶
bmap: runtime/map.go cmd/compile/internal/gc/reflect.go
type bmap struct {
topbits [8]uint8
keys [8]keytype
elems [8]elemtype
pad uintptr
overflow uintptr
}
哈希表中桶的真正结构其实是在编译期间运行的函数 bmap 中被『动态』创建的, 代码在cmd/compile/internal/gc/reflect.go
-
topbits存储hash值的高8位,通过比对高8位减少键值对访问次数以提高性能 -
keys/elems数组 -
pad内存对齐 -
overflow溢出桶,map存储数据过多时使用
实现原理
时间复杂度: O(1)
hash函数和hash冲突解决方法
hash函数
实现哈希表的关键点在于如何选择哈希函数,哈希函数的选择在很大程度上能够决定哈希表的读写性能,在理想情况下,哈希函数应该能够将不同键映射到不同的索引上,这要求哈希函数输出范围大于输入范围,但是由于键的数量会远远大于映射的范围,所以在实际使用时,这个理想的结果是不可能实现的。
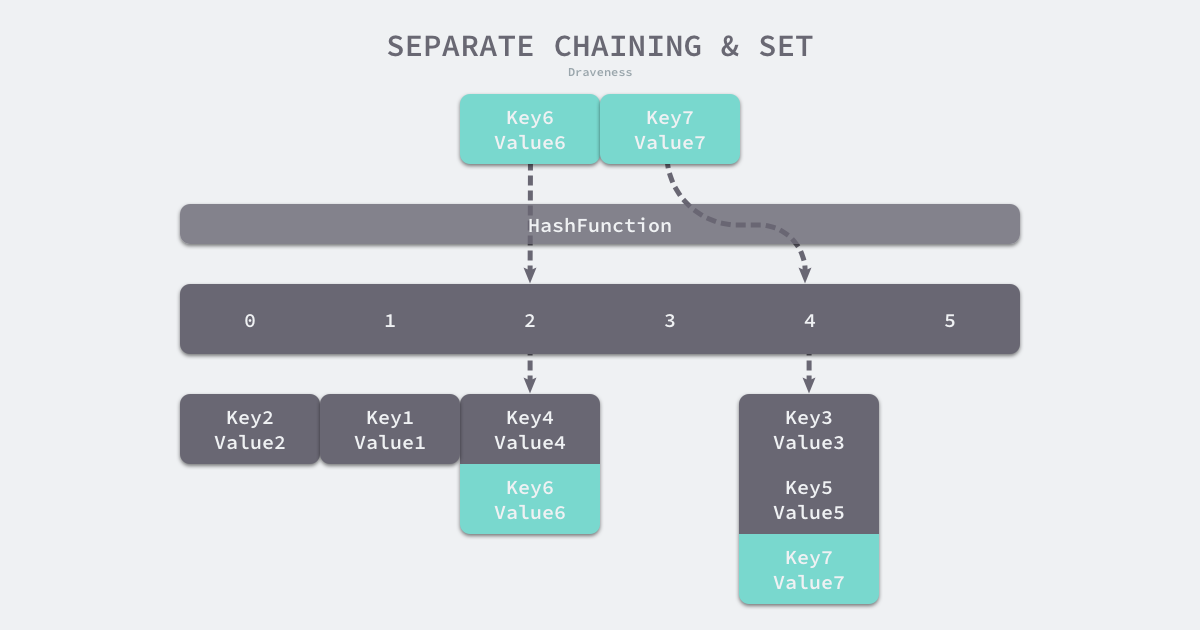
hash冲突
开放寻址法:对数组中的元素依次比较键值对是否存在于数组
拉链法: 使用数组加上链表
读写操作
读
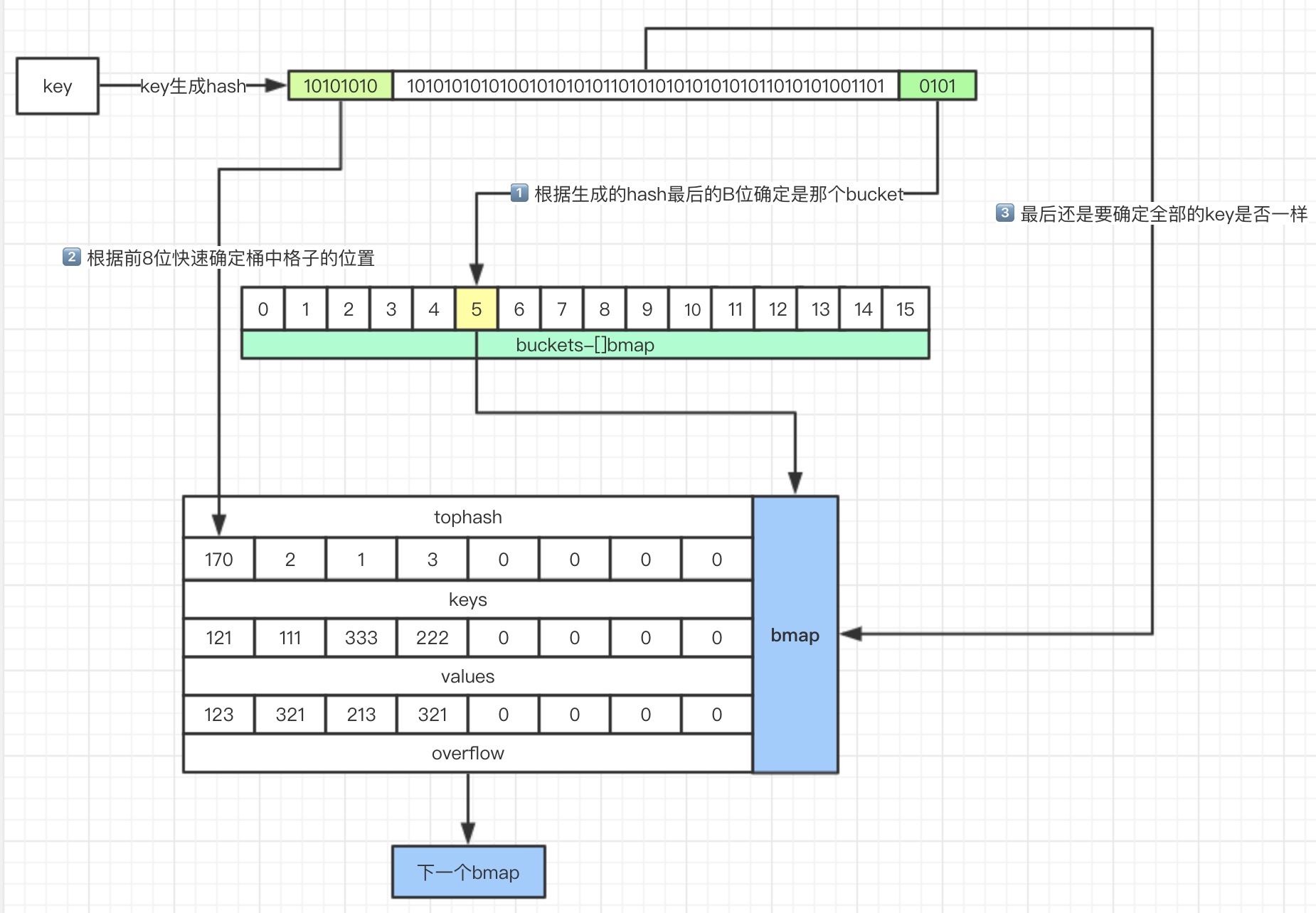
- 计算出key的hash
- 用最后的“B”位来确定在哪个桶(“B”就是前面说的那个,B为4,就有16个桶,0101用十进制表示为5,所以在5号桶)
- 根据key的前8位快速确定是在哪个格子(额外说明一下,在bmap中存放了每个key对应的tophash,是key的前8位)
- 最终还是需要比对key完整的hash是否匹配,如果匹配则获取对应value
- 如果都没有找到,就去下一个overflow找
写
- 通过key的后“B”位确定是哪一个桶
- 通过key的前8位快速确定是否已经存在
- 最终确定存放位置,如果8个格子已经满了,没地方放了,那么就重新创建一个bmap作为溢出桶连接在overflow
扩容
条件:
- 装载因子大于6.5
- 溢出桶 大于15个
func mapassign(t *maptype, h *hmap, key unsafe.Pointer) unsafe.Pointer {
...
if !h.growing() && (overLoadFactor(h.count+1, h.B) || tooManyOverflowBuckets(h.noverflow, h.B)) {
hashGrow(t, h)
goto again
}
...
}
方式:
- 等量扩容
- 翻倍扩容