go channel 也是通过共享内存和互斥锁来实现通信的
原文地址:https://www.douyacun.com/article/1fae44831307134b7c62dc5f6545032a go语言提倡的并发模型就是:不要通过共享内存的方式进行通信,而是应该通过通信的方式共享内存
目录
mind map
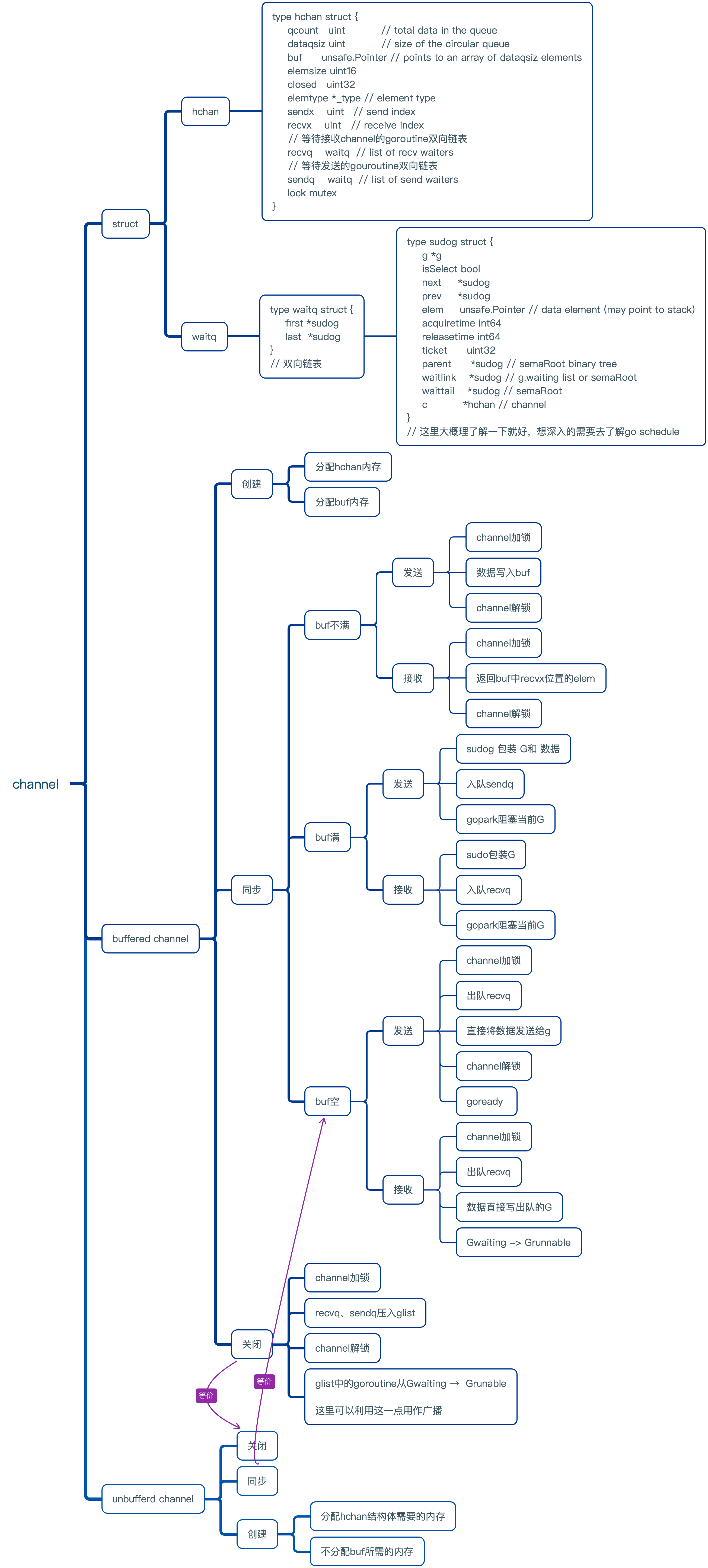
结构体
type hchan struct {
qcount uint // total data in the queue
dataqsiz uint // size of the circular queue
// buf数组,这里存储的就是发送的数据
buf unsafe.Pointer // points to an array of dataqsiz elements
elemsize uint16
// chan是否关闭
closed uint32
elemtype *_type // element type
// 数组写过队列应该明白就是为了让数组能转起来
sendx uint // send index
recvx uint // receive index
// 这里维护等待 发送/接收 goroutine
recvq waitq // list of recv waiters
sendq waitq // list of send waiters
// lock protects all fields in hchan, as well as several
// fields in sudogs blocked on this channel.
//
// Do not change another G's status while holding this lock
// (in particular, do not ready a G), as this can deadlock
// with stack shrinking.
lock mutex // 互斥锁,buf数组并不是线程安全的
}
调用栈
下面的内容都是源码分析不想深入的同学,就不要看了。chan有4个动作,相应的代码位置:
- make -> runtime/chan.makechan
- send -> runtime/chan.chansend
- recieve -> runtime/chan.chanrecv
- closed -> runtime/chan.closechan
make
func makechan(t *chantype, size int) *hchan {
elem := t.elem
// compiler checks this but be safe.
// 这里是编译器检测
if elem.size >= 1<<16 {
throw("makechan: invalid channel element type")
}
if hchanSize%maxAlign != 0 || elem.align > maxAlign {
throw("makechan: bad alignment")
}
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(elem.size, uintptr(size))
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc-hchanSize || size < 0 {
panic(plainError("makechan: size out of range"))
}
// Hchan does not contain pointers interesting for GC when elements stored in buf do not contain pointers.
// buf points into the same allocation, elemtype is persistent.
// SudoG's are referenced from their owning thread so they can't be collected.
// TODO(dvyukov,rlh): Rethink when collector can move allocated objects.
var c *hchan
switch {
case mem == 0:// 无缓存channel
// Queue or element size is zero.
c = (*hchan)(mallocgc(hchanSize, nil, true))// 无缓存channel就没必要申请buf
// Race detector uses this location for synchronization.
c.buf = c.raceaddr()
case elem.kind&kindNoPointers != 0:// 有缓存channel
// Elements do not contain pointers.
// Allocate hchan and buf in one call.
// 这里提到chan最好不要包含指针传递,并发的话会引起race
c = (*hchan)(mallocgc(hchanSize+mem, nil, true))// 结构体的大小加上buf的大小
c.buf = add(unsafe.Pointer(c), hchanSize)
// 这里画一下内存大小,chan struct中的buf指向就是后面多申请的这一块buf内存
// |chan struct|buf...|
default:
// Elements contain pointers.
c = new(hchan)
c.buf = mallocgc(mem, elem, true)
}
c.elemsize = uint16(elem.size)
c.elemtype = elem
c.dataqsiz = uint(size)
if debugChan {
print("makechan: chan=", c, "; elemsize=", elem.size, "; elemalg=", elem.alg, "; dataqsiz=", size, "\n")
}
return c
}
chan通道实际也是通过共享内存和互斥锁实现
chan最好不要传递指针
send
无缓冲channel send
// entry point for c <- x from compiled code
//go:nosplit
func chansend1(c *hchan, elem unsafe.Pointer) {
chansend(c, elem, true, getcallerpc())
}
/*
* generic single channel send/recv
* If block is not nil,
* then the protocol will not
* sleep but return if it could
* not complete.
*
* sleep can wake up with g.param == nil
* when a channel involved in the sleep has
* been closed. it is easiest to loop and re-run
* the operation; we'll see that it's now closed.
*/
func chansend(c *hchan, ep unsafe.Pointer, block bool, callerpc uintptr) bool {
// 内部检查,避免一些低级的错误发生
if c == nil {
if !block {
return false
}
gopark(nil, nil, waitReasonChanSendNilChan, traceEvGoStop, 2)
throw("unreachable")
}
if debugChan {
print("chansend: chan=", c, "\n")
}
if raceenabled {
racereadpc(c.raceaddr(), callerpc, funcPC(chansend))
}
// Fast path: check for failed non-blocking operation without acquiring the lock.
//
// 没有recv goroutine,就无法send
// channel buf 满了也是无法再次发送 todo::做着的目的是为了啥
if !block && c.closed == 0 && ((c.dataqsiz == 0 && c.recvq.first == nil) ||
(c.dataqsiz > 0 && c.qcount == c.dataqsiz)) {
return false
}
var t0 int64
if blockprofilerate > 0 {
t0 = cputicks()
}
// buf array共享内存,互斥锁来避免数据竞争
lock(&c.lock)
// send on closed channel 这句话应该见到的挺多的了
if c.closed != 0 {
unlock(&c.lock)
panic(plainError("send on closed channel"))
}
// 有goroutine等待接收channel,不需要进入buf,直接发送给等待接收的goroutine
if sg := c.recvq.dequeue(); sg != nil {
send(c, sg, ep, func() { unlock(&c.lock) }, 3) // 这里是真正发送给接收线程的操作
return true
}
// buf不满
if c.qcount < c.dataqsiz {
// chanbuf 获取当前,发送索引的内存地址
qp := chanbuf(c, c.sendx)
if raceenabled {
raceacquire(qp)
racerelease(qp)
}
// 这里是memmove(to, from, elem), 就是将ep(elem)数据写入到发送所有的地址
typedmemmove(c.elemtype, qp, ep)
// 接下来的操作就是:如何用数组来模拟一个队列
c.sendx++
if c.sendx == c.dataqsiz {
c.sendx = 0
}
c.qcount++
// 释放锁
unlock(&c.lock)
return true
}
if !block {
unlock(&c.lock)
return false
}
// buf满了,需要阻塞发送的goroutine
// Block on the channel. Some receiver will complete our operation for us.
gp := getg()
mysg := acquireSudog()
mysg.releasetime = 0
if t0 != 0 {
mysg.releasetime = -1
}
// No stack splits between assigning elem and enqueuing mysg
// on gp.waiting where copystack can find it.
mysg.elem = ep
mysg.waitlink = nil
mysg.g = gp
mysg.isSelect = false
mysg.c = c
gp.waiting = mysg
gp.param = nil
// 这上面就是阻塞并序列化当前goroutine,放到等待发送的队列中,并释放锁
c.sendq.enqueue(mysg)
// 当前goroutine的运行状态:Grunning -> Gwaiting
goparkunlock(&c.lock, waitReasonChanSend, traceEvGoBlockSend, 3)
// Ensure the value being sent is kept alive until the
// receiver copies it out. The sudog has a pointer to the
// stack object, but sudogs aren't considered as roots of the
// stack tracer.
// keepalive可以确保ep在此之前不会被gc回收
KeepAlive(ep)
// someone woke us up.
if mysg != gp.waiting {
throw("G waiting list is corrupted")
}
gp.waiting = nil
if gp.param == nil {
if c.closed == 0 {
throw("chansend: spurious wakeup")
}
panic(plainError("send on closed channel"))
}
gp.param = nil
if mysg.releasetime > 0 {
blockevent(mysg.releasetime-t0, 2)
}
mysg.c = nil
// 释放goroutine
releaseSudog(mysg)
return true
}
close
func closechan(c *hchan) {
if c == nil {
panic(plainError("close of nil channel"))
}
// channel 加锁
lock(&c.lock)
if c.closed != 0 {
unlock(&c.lock)
panic(plainError("close of closed channel"))
}
if raceenabled {
callerpc := getcallerpc()
racewritepc(c.raceaddr(), callerpc, funcPC(closechan))
racerelease(c.raceaddr())
}
// 标记channel已经关闭了
c.closed = 1
// 这里声明一个链表,收集send/recv队列中的G,方便
var glist gList
// release all readers
for {
sg := c.recvq.dequeue()
if sg == nil {
break
}
if sg.elem != nil {
typedmemclr(c.elemtype, sg.elem)
sg.elem = nil
}
if sg.releasetime != 0 {
sg.releasetime = cputicks()
}
gp := sg.g
gp.param = nil
if raceenabled {
raceacquireg(gp, c.raceaddr())
}
// glist收集所有等待接收的goroutine
glist.push(gp)
}
// release all writers (they will panic)
for {
sg := c.sendq.dequeue()
if sg == nil {
break
}
sg.elem = nil
if sg.releasetime != 0 {
sg.releasetime = cputicks()
}
gp := sg.g
gp.param = nil
if raceenabled {
raceacquireg(gp, c.raceaddr())
}
// // glist收集所有等待发送的goroutine
glist.push(gp)
}
// channel解锁
unlock(&c.lock)
// Ready all Gs now that we've dropped the channel lock.
for !glist.empty() {
gp := glist.pop()
gp.schedlink = 0
// glist中的所有goroutine从Gwaiting -> Grunable
goready(gp, 3)
}
}
receive
// chanrecv receives on channel c and writes the received data to ep.
// ep may be nil, in which case received data is ignored.
// If block == false and no elements are available, returns (false, false).
// Otherwise, if c is closed, zeros *ep and returns (true, false).
// Otherwise, fills in *ep with an element and returns (true, true).
// A non-nil ep must point to the heap or the caller's stack.
func chanrecv(c *hchan, ep unsafe.Pointer, block bool) (selected, received bool) {
// 这一块和发送的时候是一样的属于编译器的检查
if debugChan {
print("chanrecv: chan=", c, "\n")
}
if c == nil {
if !block {
return
}
gopark(nil, nil, waitReasonChanReceiveNilChan, traceEvGoStop, 2)
throw("unreachable")
}
if !block && (c.dataqsiz == 0 && c.sendq.first == nil ||
c.dataqsiz > 0 && atomic.Loaduint(&c.qcount) == 0) &&
atomic.Load(&c.closed) == 0 {
return
}
var t0 int64
if blockprofilerate > 0 {
t0 = cputicks()
}
// channel加锁
lock(&c.lock)
if c.closed != 0 && c.qcount == 0 {
if raceenabled {
raceacquire(c.raceaddr())
}
unlock(&c.lock)
if ep != nil {
typedmemclr(c.elemtype, ep)
}
return true, false
}
// 给接收者发送element
if sg := c.sendq.dequeue(); sg != nil {
// Found a waiting sender. If buffer is size 0, receive value
// directly from sender. Otherwise, receive from head of queue
// and add sender's value to the tail of the queue (both map to
// the same buffer slot because the queue is full).
recv(c, sg, ep, func() { unlock(&c.lock) }, 3)
return true, true
}
// buf不为空
if c.qcount > 0 {
// Receive directly from queue
qp := chanbuf(c, c.recvx)
if raceenabled {
raceacquire(qp)
racerelease(qp)
}
if ep != nil {
// 将buf c.recvx位置的数据copy到ep内存上
typedmemmove(c.elemtype, ep, qp)
}
typedmemclr(c.elemtype, qp)
// 等价 c.recvx = (c.recvx + 1) % c.dataqsiz
c.recvx++
if c.recvx == c.dataqsiz {
c.recvx = 0
}
c.qcount--
// channel解锁
unlock(&c.lock)
return true, true
}
if !block {
unlock(&c.lock)
return false, false
}
// no sender available: block on this channel.
// 没有接收者,阻塞当前goroutine,压入c.recvq
gp := getg()
mysg := acquireSudog()
mysg.releasetime = 0
if t0 != 0 {
mysg.releasetime = -1
}
// No stack splits between assigning elem and enqueuing mysg
// on gp.waiting where copystack can find it.
mysg.elem = ep
mysg.waitlink = nil
gp.waiting = mysg
mysg.g = gp
mysg.isSelect = false
mysg.c = c
gp.param = nil
c.recvq.enqueue(mysg)
// 当前goroutine的状态: Grunning -> Gwaiting
goparkunlock(&c.lock, waitReasonChanReceive, traceEvGoBlockRecv, 3)
// someone woke us up
if mysg != gp.waiting {
throw("G waiting list is corrupted")
}
gp.waiting = nil
if mysg.releasetime > 0 {
blockevent(mysg.releasetime-t0, 2)
}
closed := gp.param == nil
gp.param = nil
mysg.c = nil
// 释放当前groutine
releaseSudog(mysg)
return true, !closed
}